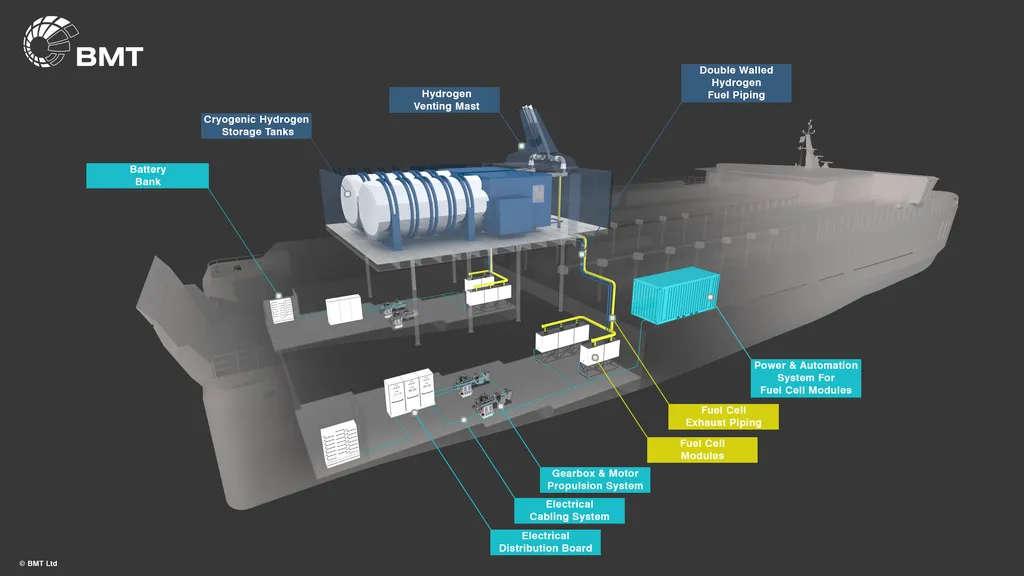
In a significant stride towards sustainable maritime propulsion, a recent study published in the International Journal of Renewable Energy Development, or *Jurnal Pengembangan Energi Terbarukan* in English, has explored the potential of hydrogen as a fuel for internal combustion engines. Led by Diep Ngoc Long Huynh from the Institute of Engineering at HUTECH University in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, the research delves into the feasibility of hydrogen as a clean alternative to traditional marine fuels.
The study, titled “Using hydrogen as potential fuel for internal combustion engines: A comprehensive assessment,” examines the chemical properties of hydrogen and its benefits over conventional fuels. Hydrogen’s high energy content and clean combustion properties make it an attractive option for the maritime industry, which is under increasing pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and meet sustainability goals.
Huynh and his team have looked into the technological advancements and modifications required for both compression ignition and spark ignition engines to efficiently utilize hydrogen. They’ve also addressed the environmental impacts, including reductions in greenhouse gases and other pollutants, and evaluated the economic implications, such as production costs and feasibility compared to other energy solutions.
One of the key challenges highlighted in the study is the storage, distribution, and safety of hydrogen. However, the research also discusses potential solutions and innovations currently under investigation, offering a glimpse into the future of hydrogen-powered maritime propulsion.
“The maritime industry is at a crossroads,” says Huynh. “We need to explore alternative fuels that can help us meet our net-zero goals without compromising on performance or safety. Hydrogen presents a promising opportunity, but there are still challenges to overcome.”
The study provides a thorough understanding of the current state of hydrogen as a fuel for internal combustion engines, guiding future research and development in this vital field. For maritime professionals, this research opens up new avenues for exploration and investment, with the potential to revolutionize the way ships are powered.
As the industry continues to grapple with the challenges of decarbonization, hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines could emerge as a viable solution, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional marine fuels. The study by Huynh and his team is a significant step forward in this journey, providing valuable insights and guidance for the maritime sector’s transition to a greener future.
In the words of Huynh, “The future of maritime propulsion is not just about finding a cleaner fuel; it’s about finding a fuel that can power our ships efficiently, safely, and sustainably. Hydrogen has the potential to be that fuel, and we’re just scratching the surface of what’s possible.”