In a significant stride towards enhancing data analysis in fields like medicine and environmental science, researchers have introduced a new method to improve the accuracy of statistical models used to analyze data bounded between 0 and 1. This development, led by Ali T. Hammad from the Department of Mathematics at Tanta University in Egypt, focuses on the beta regression model (BRM), a tool widely applied in various scientific disciplines. The research, published in the journal ‘Applied Mathematics in Science and Engineering’, addresses critical issues that can skew results and lead to flawed decision-making.
The beta regression model is a go-to for analyzing data that falls within the open interval (0, 1), such as proportions, rates, and probabilities. However, traditional methods of estimating parameters in these models, like the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE), can be thrown off by multicollinearity—when predictor variables are highly correlated—and outliers, which can bias estimates and inflate errors. Hammad and his team have developed new robust ridge-type estimators designed to mitigate these issues.
“Our proposed estimators offer a more reliable and robust alternative to existing methods, especially when dealing with multicollinear and outlier data,” Hammad explained. The team’s theoretical comparisons and simulation studies under various conditions consistently showed that their estimators outperformed traditional MLE and existing robust ridge estimators in the presence of multicollinearity and outliers.
For maritime professionals, the implications of this research are substantial. In an industry where data analysis is crucial for everything from route optimization to environmental impact assessments, robust statistical methods can lead to more accurate predictions and better decision-making. For instance, analyzing water quality data or fuel efficiency metrics often involves dealing with data that falls within the 0 to 1 range. The new estimators can help ensure that the insights drawn from such data are reliable, even when the data is messy or incomplete.
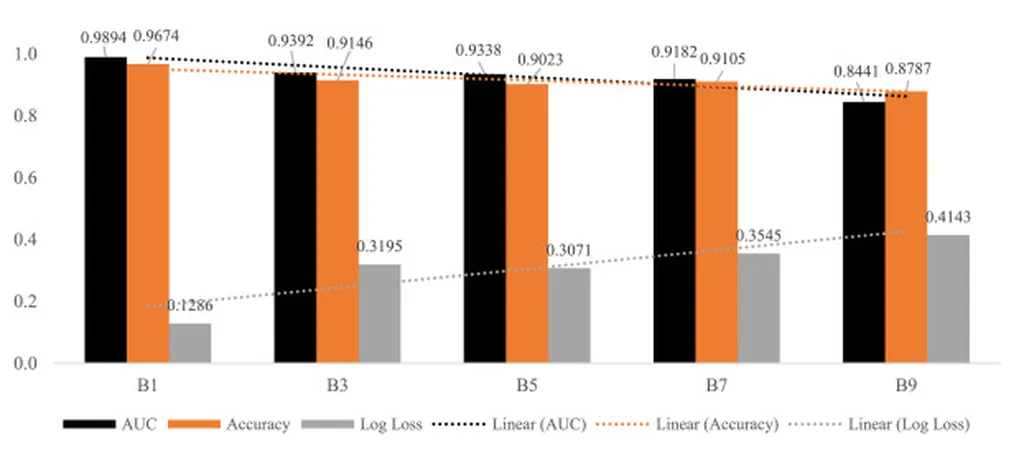
The practical utility of these methods was further validated through an application to a real-world dataset on breast cancer data, demonstrating their effectiveness in empirical research. This underscores the importance of using robust biased estimation techniques to enhance the accuracy and reliability of regression models.
As Hammad noted, “The results emphasize the importance of using robust biased estimation techniques to enhance the accuracy and reliability of regression models, especially in empirical research involving multicollinear and outlier data.” For maritime sectors, adopting such advanced statistical methods can lead to more efficient operations, better risk management, and improved compliance with environmental regulations.
In summary, the new robust ridge-type estimators developed by Hammad and his team represent a significant advancement in statistical modeling. By addressing the challenges of multicollinearity and outliers, these estimators provide a more reliable tool for data analysis, benefiting a wide range of industries, including maritime. As the field of data science continues to evolve, such innovations will be crucial in ensuring that the insights derived from data are both accurate and actionable.