In a significant stride towards enhancing traffic management systems, researchers have developed a novel approach that leverages the power of graph neural networks to estimate traffic states more accurately. This innovative method, published in the journal ‘Sensors’ (translated from the Chinese title), integrates traffic flow theory into a cutting-edge estimation framework, offering promising applications for maritime and transportation sectors.
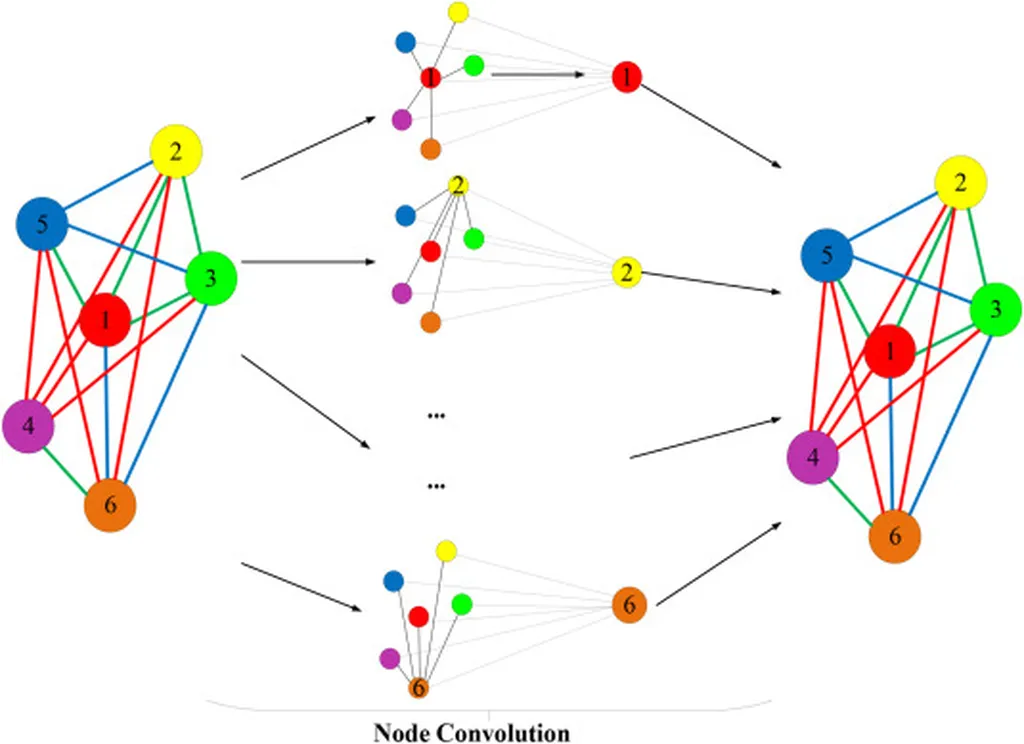
At the helm of this research is Xiwen Lou, a faculty member at the Faculty of Maritime and Transportation, Ningbo University, China. Lou and his team have tackled the challenge of traffic state estimation (TSE), a critical component for intelligent transportation systems. TSE provides unobserved parameters essential for effective traffic management and control. The team’s novel approach involves constructing wave-informed anisotropic temporal graphs to capture time-delayed correlations across road networks, which are then merged with spatial graphs into a unified spatiotemporal structure.
One of the standout features of this research is the use of a four-layer diffusion graph convolutional network. Each layer is enhanced with a squeeze-and-excitation attention mechanism, allowing the model to adaptively capture dynamic directional correlations. Lou explained, “This adaptive mechanism is crucial as it enables the model to focus on the most relevant information, improving its accuracy in estimating traffic states.”
The researchers also introduced the fundamental diagram equation into the loss function, guiding the model towards physically consistent estimations. This integration of traffic flow theory ensures that the model’s predictions are not only mathematically sound but also align with real-world traffic dynamics.
The commercial impacts of this research are substantial. Accurate traffic state estimation can lead to more efficient traffic management, reduced congestion, and improved safety. For the maritime sector, this technology can be particularly beneficial in port areas and logistics hubs, where traffic management is crucial for maintaining smooth operations. By integrating this technology, ports can optimize the flow of goods and vehicles, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
Moreover, the ability to capture complex traffic dynamics can provide valuable insights for urban planning and infrastructure development. Cities can use this technology to design better road networks, improve public transportation systems, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
Lou’s research has demonstrated that the proposed model achieves higher accuracy than benchmark methods, confirming its effectiveness in capturing complex traffic dynamics. This breakthrough opens up new opportunities for the maritime and transportation sectors to leverage advanced technologies for better traffic management and control.
As the world moves towards smarter and more connected transportation systems, innovations like this are paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future. With the publication of this research in ‘Sensors’, the scientific community now has a robust framework to build upon, driving further advancements in traffic state estimation and intelligent transportation systems.
For maritime professionals, this research highlights the potential of integrating advanced technologies into traffic management systems. By adopting these innovations, ports and logistics hubs can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety, ultimately contributing to a more seamless and sustainable maritime industry.