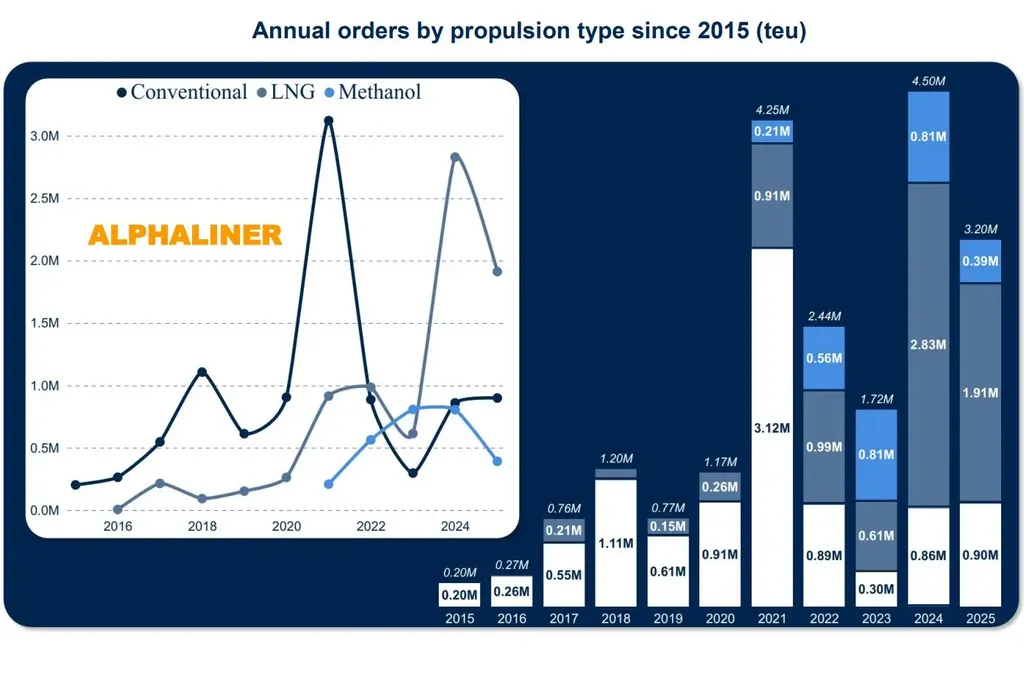
The maritime industry’s fuel mix is evolving at pace, with LNG, methanol, and biofuels leading the charge in 2025. LNG retained its crown as shipping’s most widely adopted alternative fuel, with 407 merchant and leisure vessel orders set to deliver LNG-capable ships. The fuel’s appeal lies in its immediate carbon dioxide emissions reductions, as confirmed by LR’s Fuel for Thought: LNG report. However, the industry must tackle methane slip and accelerate the transition towards bio-LNG and synthetic LNG variants to align with longer-term decarbonisation objectives.
Methanol-capable vessels also gained traction, with 134 orders in 2025, accounting for a significant portion of the alternative-fuelled orderbook. In July, LR updated its Rules and Regulations for Ships Using Gases or Other Low-flashpoint Fuels to reflect evolving safety expectations and align with the IMO IGF Code, strengthening the regulatory foundation for methanol as a marine fuel.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), another established alternative fuel, saw 24 additional LPG-capable vessels ordered. While LPG carrier vessels are the primary users of this fuel, there remains potential for adoption by other vessel types.
Ammonia and hydrogen are also gaining momentum. There were six orders for ammonia-fuel capable vessels, with progress made in approvals in principle for ammonia-ready designs and ongoing work to address production capacity and regulatory advancement. Hydrogen maintained momentum with 13 hydrogen capable orders, with fuel cells powered by hydrogen viewed as options for achieving zero or near net-zero tank-to-wake emissions. LR’s updated guidance for the installation of fuel cells on ships incorporates recent regulatory updates and technical developments related to fuel cell technology in the maritime sector.
Biofuels strengthened their position as a practical, near-term solution for emissions reduction, particularly within existing fleets, with 11 biofuel-capable newbuild orders. The diversity and quality of biofuels are growing, with uptake of FAME-based biofuel blends, notably B30 RF, increasing across ports including Singapore, Algeciras and Antwerp. In April, LR’s Global Fuel Finder tool added biofuel availability and quality insights to the platform, helping users search, compare and analyse biofuels across global ports. Earlier in the year, operator John H Whitaker Tankers launched Whitchampion, the first bunker tanker certified to load, carry and blend FAME B100 biofuel on board. The IMO also issued improved guidance on carrying biofuel blends by bunker ships, with interim guidelines outlining new requirements for alternative fuel systems, operational risk assessments, and the handling of biofuel blends.
While nuclear remains a longer-term and highly regulated prospect, LR continued to explore its potential applications within the maritime sector. A partnership with Microsoft (via Azure OpenAI) will see generative AI used to accelerate permitting/licencing processes for maritime nuclear applications. LR also joined a global cross-industry pledge to triple nuclear energy capacity by 2050 and published Navigating Nuclear Energy in Maritime, the industry’s first guidance document for nuclear-powered shipping.
This diverse fuel landscape presents both opportunities and challenges. As the industry navigates the transition to a low-carbon future, collaboration, innovation, and regulatory support will be key to unlocking the full potential of these alternative fuels.